Docks
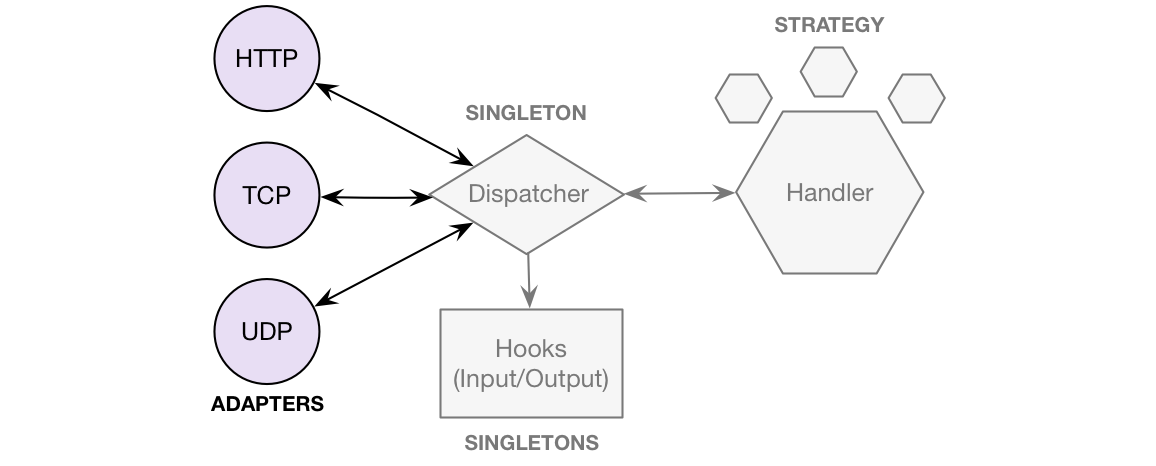
Description
Listens to a single port for incoming messages through a specific protocol and parses it into a plain javascript object. Then passes this object along to the dispatcher. If a response comes back, the dock serializes it to match the message format and sends it off to the original device.
Docks must extend the base Dock class.
Exposed Methods
Methods that must be implemented
- listen() - Starts listening to the configured port. Should call
process(). - stop() - Stops listening to the port.
- send(response) (optional) - Sends the response to the original device.
Methods present in the base class
-
validate(message) - Validates the message length against the configured max and performs a format check. This method can be overriden if needed. Returns
trueif valid,falseotherwise. -
parse(data, meta) - Parses the message and converts it to a javascript object. This is a default implementation provided for convenience that can and should be overriden to suit your needs. Returns the parsed data object or
falseif the message couldn't be parsed.Sample message
tag1|subtag1|02,56,58,8|subtag2|sds,sd,wtr,ghdStructure of the parsed data object
This format is the standard for passing data through Iris components.
{ tag: // A string, the message tag meta: // An object with additional data, such as the IP address that the message came from // Must be set by the child class data: // An object with the actual parsed data }Sample
metapropertymeta: { ip: '127.0.0.1' }Sample
datapropertydata: { subtag1: ['02', '56', '58', '8'], subtag2: ['sds', 'sd', 'wtr', 'ghd'] } -
process(message, meta, callback) - Calls
validate()andparse()and sends the result to the dispatcher. Should be called bylisten(). The callback is optional and will be called with the response if the handler produces one. -
encode(response) - Serializes the response. This is a default implementation provided for convenience that can and should be overriden to suit your needs. Returns the encoded message or
falseif the encoding was unsuccessful.How it works:
- If the response is a string: will leave it alone.
- If the response is an array: will join it.
- If the response is a plain object: will try to use the values with the keys as subtags, following the default message format
|subtag1|value1,value2|subtag2|value3,value4,value5. - Otherwise, if the response has a toString() method: will call it and leave the output alone.
The separators can be configured, just like with the parser.
-
reply(response) - If
send()if defined, callsencode()and pipes the result tosend().
Exposed Properties
Getters that must be implemented
-
path (string) - Returns the path of the dock file.
Sample implementation
get path() { return __filename; }
Getters present in the base class
- id (string) - Returns the dock id, an unique string that is autogenerated every time the app runs.
- name (string) - Returns the dock name.
- protocol (string) - Returns the dock protocol.
- port (integer) - Returns the configured port.
- config (string) - Returns the config object.
Setters present in the base class
- config (string) - Sets the config object.
Events
const dock = require('iris-dock-myAwesomeDock');
dock.on('data', function(event){
console.log('data', event.data);
});
Every event object contains the following properties:
- target - The dock that triggered the event.
- data - A data object.
Emits
- data-hookname - Triggered every time the dock receives a new message. Gives the handler access to the raw, unprocessed data. Useful to proxy it somewhere else.
- response-hookname - When the dock receives a response from the dispatcher.
- invalidMessage-hookname - Triggered when a message does not pass
validate()filters, or when the message either is not a string, or does not have atoString()method.
Configuration
{
port: 5000,
parser: {
subtagSeparator: '#', // example, default is |
dataSeparator: '.' // example, default is ,
},
encoder: {
subtagSeparator: '#', // idam parser
dataSeparator: '.' // idem parser
},
maxMessageLength: 100
}
- port (integer) - The port to listen to.
- parser (object, optional) - If you're using the default parser, you can configure the subtag and data separators. The defaults are
|forsubtagSeparatorand,fordataSeparator. - encoder (object, optional) - Idem parser.
- maxMessageLength (integer, optional) - The max length in characters of a message. If not set, the default is
300.