Hooks
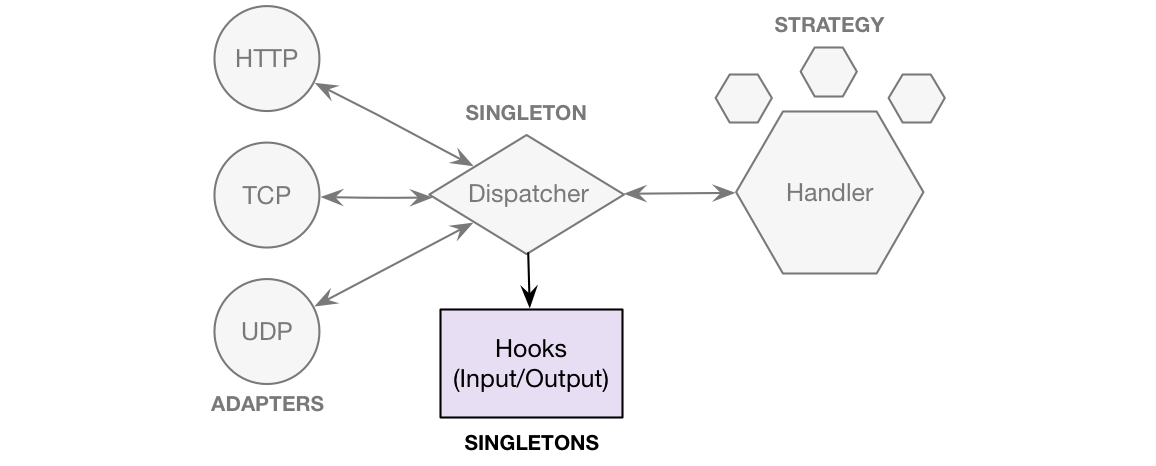
Description
A hook is just a callback function that gets executed whenever a piece of data passes by the dispatcher in the course of a data flow. Multiple hooks can be tied to a single flow. Each hook can be set to run when the message object comes in (input hook) or when the response goes out (output hook).
Hooks must extend the base Hook class.
Difference with handlers
The handler can generate and return a response. Hooks can run on the response as well on the data.
Exposed Methods
Methods that must be implemented
- process(data) - The hook body, the function that will be executed.
Methods present in the base class
- run(data) - Receives the data from the dispatcher and calls
process().
Exposed Properties
Getters that must be implemented
-
path (string) - Returns the path of the hook file.
Sample implementation
get path() { return __filename; }
Getters present in the base class
- name (string) - Returns the handler name.
- config (string) - Returns the config object.
Setters present in the base class
- config (string) - Sets the config object.
Events
const hook = require('iris-hook-myAwesomeHook');
hook.on('data', function(event){
console.log('data', event.data);
});
Every event object contains the following properties:
- target - The hook that triggered the event.
- data - A data object.
Emits
- data-hookname - Triggered every time the hook receives a new piece of data/response.